At TORALOGI, we have covered various logistics robots, which are among the digital transformation solutions that have garnered attention in the logistics industry. In a recent article (Introduction of the Latest Logistics Robots Active in Logistics Warehouses – ② Shipping (Picking (Piece Picking))), we featured a wide range of robots that support picking operations, and introduced the Picking Assist AMR as one of them.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the Picking Assist AMR, discussing its current status and the increasing number of cases where it is being utilized to improve productivity with a smaller investment compared to other robot solutions.
To accommodate the volume of information, we have divided this article into two parts, Part I and Part II. In the first part, we will cover the following topics:
・Definition of AMR
・Market conditions up to the present
・Major solutions
・Differences from other logistics robots
In the second part of this article, we will clearly explain the specific benefits of utilizing the Picking Assist AMR and examine the balance between the benefits and the investment required.
we will examine in detail the benefits that arise from using…
- 1 What is AMR and what is Picking Assist AMR?
- 2 Status of Picking Assist AMR Introduction in Japan
- 3 Major Solutions
- 4 Comparison of Picking Assist AMR with other robotic solutions
- 4.1 Picking Assist AMRs are at the forefront of “picking transport robots” used in logistics operations.
- 4.2 Features of Picking Assist AMR (1) Relatively small installation cost
- 4.3 Features of Picking Assist AMR (2) Easy to implement (minimal impact on operations, short time required)
- 4.4 A quick and effective solution that serves as an entry point for utilizing robots in small to medium-sized operations.
What is AMR and what is Picking Assist AMR?
AMR stands for Autonomous Mobile Robot, as the name suggests, this type of robot moves autonomously by itself.
Comparing it to AGVs (Automatic Guided Vehicles) is perhaps the easiest way to understand. AGVs require some form of guide (such as magnetic tape on the floor, stickers on the floor/walls, or lasers) to move and can only operate within the guide’s limits. On the other hand, AMRs have their own map information and can determine their location within it. They can autonomously navigate and choose their own route while using sensors to detect obstacles. In environments where people and other objects need to move simultaneously with the robots, AGVs may struggle to adapt, and AMRs with more advanced mobility are better suited for the task.
Currently, AMRs are mainly utilized in the logistics industry for picking operations. For example, the PA-AMR (Pick Assist Autonomous Mobile Robot) offered by the leading AMR provider in logistics, Rapyuta Robotics, is designed to efficiently navigate through environments with irregularly placed objects like shelves, carts, ladders, and products stored outside of the designated storage areas. By autonomously determining the most efficient route, AMRs are able to move safely and effectively in dynamic environments. As they can safely collaborate and cooperate with humans, AMRs are also known as collaborative robots or cobots.
In this article, we will introduce the “picking assist AMR,” an AMR that assists with picking. Although it is mainly used for picking, it can also be used for the opposite task of shelving goods. Furthermore, in the future, AMR is expected to be used in a wider range of areas, such as in cooperation with forklifts.
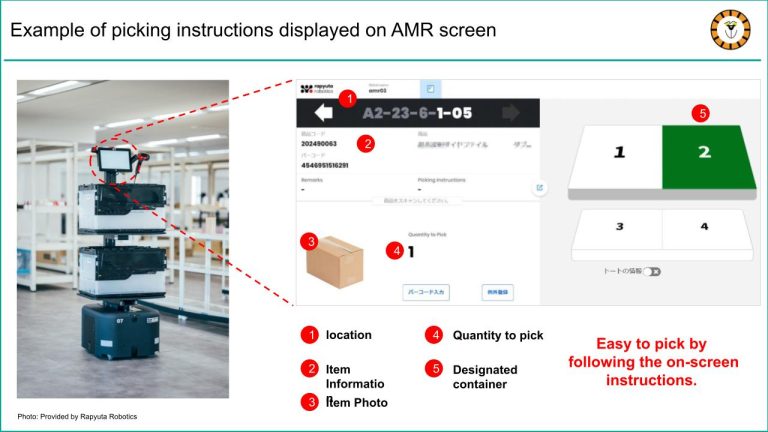
 Image: provided by Rapyuta Robotics
Image: provided by Rapyuta Robotics
Status of Picking Assist AMR Introduction in Japan
As of 2022, there are around 4-5 companies that are focusing on developing solutions for picking assist AMRs (excluding those who act as distributors for the same solutions, and those who have just started their businesses and are not yet fully engaged in deployment). In the next part, we will introduce some of the typical solutions.
The introduction of picking assist AMRs by several manufacturers started around 2020. As of 2022, dozens of companies have adopted the technology, and it is likely to reach around 50 companies in the near future. Adoption has been observed not only in large companies, but also in medium-sized and smaller ones. It is expected that the base of users will continue to expand, and the adoption pace will further increase in the future.
Major Solutions
This section provides an overview of the major solutions of Picking Assist AMR. We will limit ourselves to a brief introduction here, as it has already been presented in detail in a separate article that we have already mentioned earlier. We hope you enjoy the second part of this article, which will focus on a deeper look at the benefits of these AMR solutions.
Rapyuta PA-AMR (Rapyuta Robotics)
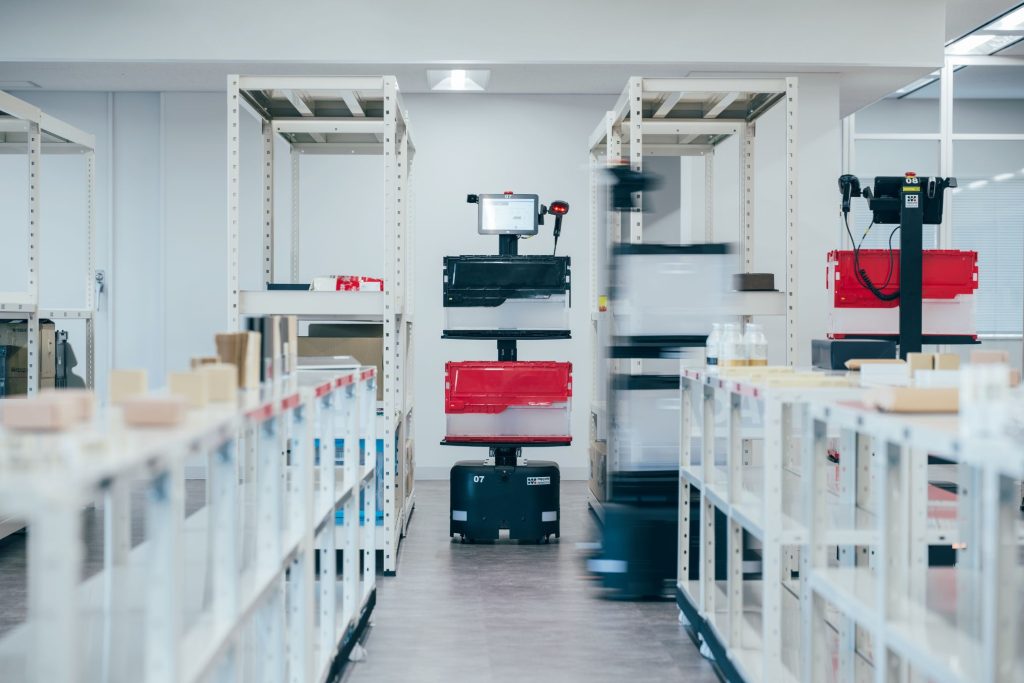


Source: Rapyuta Robotics website
Rapyuta Robotics is the leading provider of Picking Assist AMR solutions. It is one of the companies that you must consult with if you are considering introducing AMRs. When I first saw Rapyuta Robotics’ Picking Assist AMR in 2021, I was truly impressed by its smooth operation, speed, attention to safety, user-friendly display, and other features that exceeded expectations. Others who saw it together also expressed their admiration, saying “it’s really smart.” It was evident that they intuitively recognized its high practicality.
Rapyuta PA-AMR (Rapyuta Robotics) Introduction Page
FlexComet, FlexSwift(Syrius)
 Source: Syrius website
Source: Syrius website
Syrius is a Chinese robot manufacturer. With its track record in China, Syrius is promoting the use of picking-assist AMR in Japan, including the early development of the Raas (Robotics as a Service) model, in which robots are leased on a subscriber basis.
FlexComet (Syrius) Introduction Page
PEER(Ground)
GROUND Inc. is a Japanese logistics solutions provider with strengths in the latest technologies such as robots and WES (Warehouse Execution System). GROUND offers the PEER and an RFID-compatible version of its PEER SpeeMa+™ picking-assist AMR.
PEER (Ground) Introduction Page
Locus Robotics
Source: Locus Robotics website
Locus Robotics is a US-based robotics company for logistics warehouses and one of the leading AMR companies globally. It offers an AMR called “LocusBots.” The company has announced that it will make its first entry in Japan in January 2023.
Locus Robotics introduction page
AI picking cart (Teraoka)

Source: Teraoka website
Teraoka offers the AI Picking Cart, a picking assist AMR equipped with a function that performs weight inspection during picking.
AI Picking Cart (Teraoka) Introduction Page
Comparison of Picking Assist AMR with other robotic solutions
Picking Assist AMRs are at the forefront of “picking transport robots” used in logistics operations.
In a previous article that surveyed and compiled various logistics robots used in warehouses, particularly in the shipping (picking) phase, we attempted to classify “picking transport robots” into six types. AMRs were featured as type 1 and are considered the top performer. All types of picking robots can improve productivity compared to manual picking tasks, but they differ in optimizing travel routes, storage efficiency, implementation costs, and other factors. One of the significant advantages of Picking Assist AMRs is that (1) the implementation cost is relatively low compared to other logistics robots, and (2) they are easy to introduce without significant impact on operations and can be done in a short period.
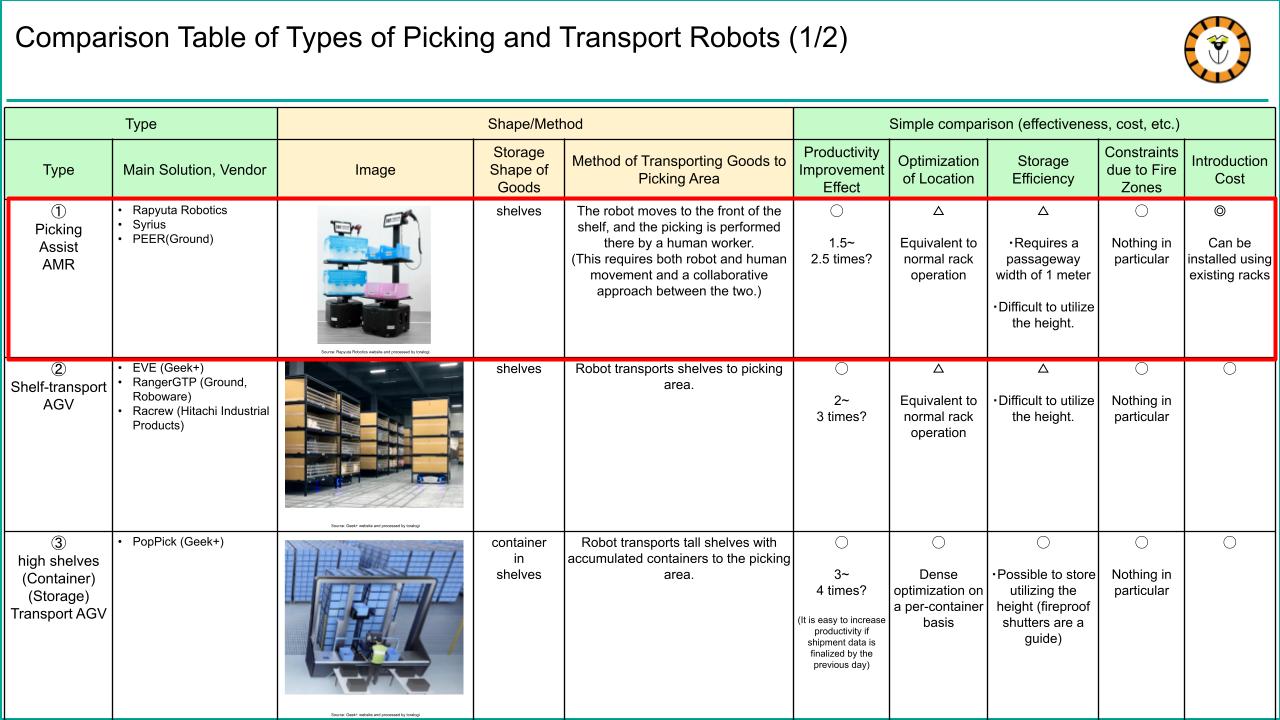
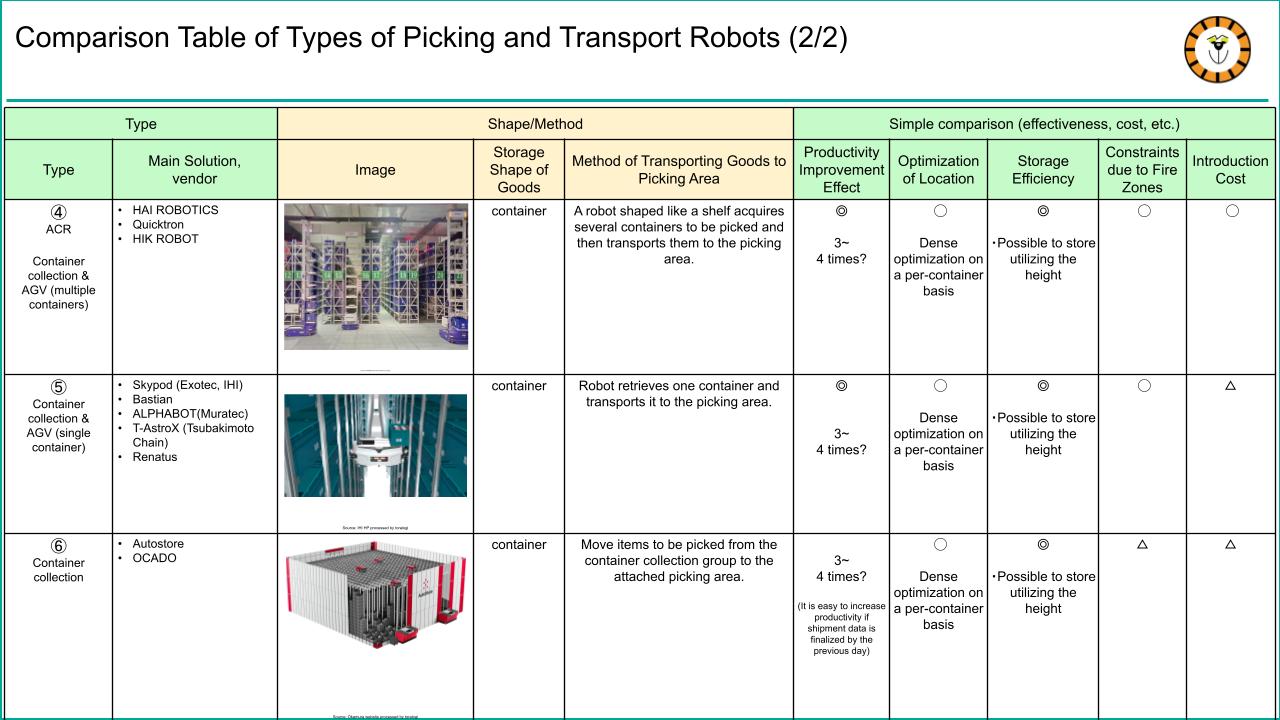
Features of Picking Assist AMR (1) Relatively small installation cost
The Picking Assist AMR differs from other robots in its concept of collaboration with humans to “significantly reduce” the distance they travel. In contrast, other robots aim to eliminate human walking distance. This robot is smaller and more agile, resulting in lower implementation costs than other larger robots (Types 2-6). Furthermore, the Picking Assist AMR moves between racks where items are stored and can generally adapt to any type of rack. Therefore, users can utilize their existing rack facilities without requiring dedicated rack equipment, making it easier to control costs compared to other types of robots. Later, we’ll go into more detail about how the robot collaborates with humans to achieve increased productivity.
Features of Picking Assist AMR (2) Easy to implement (minimal impact on operations, short time required)
It is possible to introduce picking assist AMRs while continuing warehouse operations as usual, as existing rack facilities can be utilized as they are. The setup period for introducing picking assist AMRs on-site is also relatively short, typically taking around a month. Although network and infrastructure work may also be necessary, this can be carried out without affecting on-site operations, prior to setting up the picking assist AMRs.
In contrast, other types of robots involve more extensive equipment changes and construction work, resulting in a longer construction period and a longer impact on the continuation of on-site operations. It is likely that more robots will be installed in newly constructed distribution centers than in existing distribution centers as equipment changes.
In the spring of 2022, we spoke with Rapyuta Robotics, the vendor of the AMR picking assist system, who told us that the percentage of inquiries to the company was roughly 50-50 between existing centers and new centers.
A quick and effective solution that serves as an entry point for utilizing robots in small to medium-sized operations.
The Picking Assist AMR, which can be easily introduced with low installation costs, is considered a promising option as a quick improvement measure. There are other robots that can be expected to have a greater impact on productivity improvement, but their investment costs are higher, and users who can take the plunge to introduce them are currently more limited. The Picking Assist AMR may also be a good starting point for those who want to utilize robots and embark on digital transformation.
In this article, we provided a definition and overview of picking assist AMR, which seems to have become established as a type of logistics robot that is becoming increasingly popular. In the second part, we will discuss the specific merits of AMR in more detail. Please take a look at the second part as well.
we will examine in detail the benefits that arise from using…